W prestiżowym czasopiśmie Tuexenia (nazwa od jednego z najbardziej wpływowych geobotaników, Reinholda Tuexena), zespół prof. Arkadiusza Nowaka przedstawia schemat syntaksonomiczny roślinności halofitycznej dla obszaru Pamiro-Ałąju i zachodniego Tienszanu.
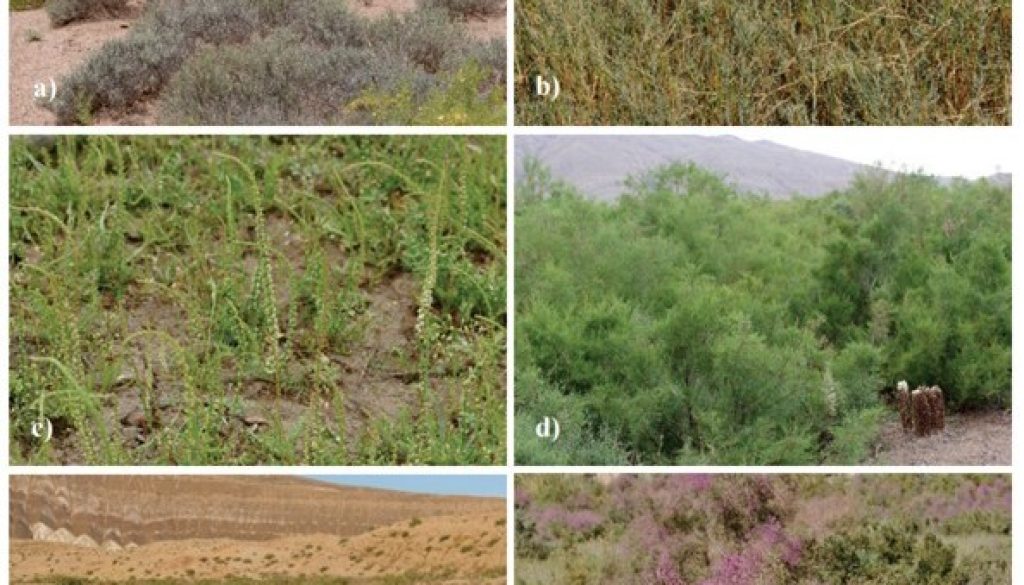
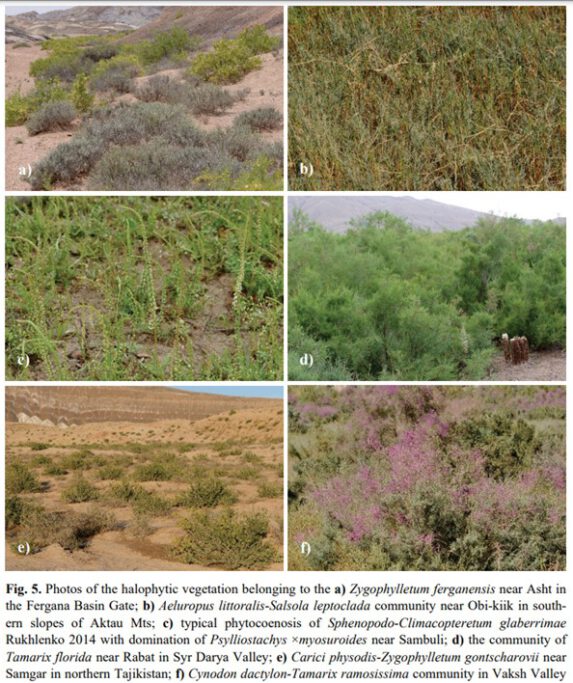
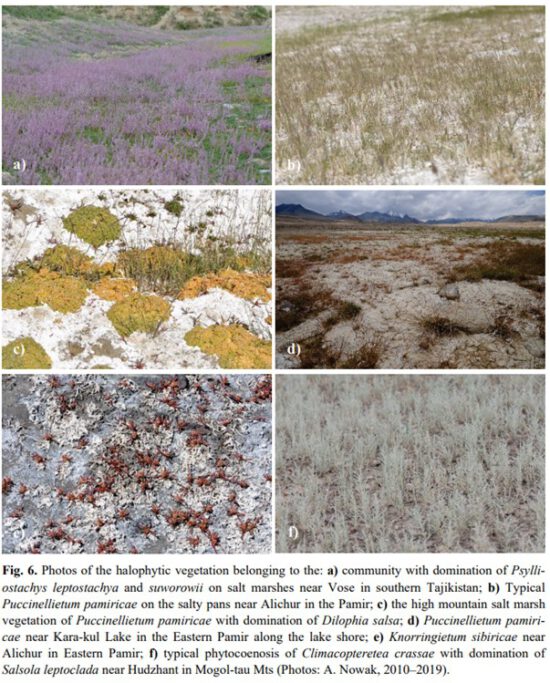
Na badanym obszarze wyróżniono halofityczne zbiorowiska krzewów, trzy efemeryczne, zalewane murawy halofityczne i jedno zbiorowisko nadbrzeżne. Cztery zbiorowiska zostały zdefiniowane jako nowe zespoły roślinne: Knorringietum sibiricae, Puccinellietum pamiricae, Carici physodis, Zygophylletum gontscharovii i Zygophylletum ferganensis. Dodatkowo z wschodniego Pamiru opisano nowy związek Taraxacion murgabici oraz nowy rząd roślinności halofitycznej Psylliostachyetalia spicato-leptostachyae.
Głównymi czynnikami różnicującymi skład gatunkowy badanej roślinności jest udział i liczba gatunków jednorocznych i bylin, pokrycie warstwy krzewów, liczba i udział elementów irano-turańskich, średnia roczna temperatura i wysokość nad poziomem morza.
Abstract:
In this paper, we complete the syntaxonomical scheme for halophytic vegetation and adjoining plant communities of the lowland, montane and alpine zones in the Pamir-Alai and western Tian Shan in Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan with some remarks on its environmental predictors. A total of 217 relevés were sampled in 2014–2019 using the seven-degree cover-abundance scale of the Braun-Blanquet approach. Modified TWlNSPAN was used to classify plant communities based on species composition. The cover-abundance scale was transformed using the four-step interval scale with cut-off levels at 0%, 5% and 25%. Diagnostic species were identified using the phi coefficient as a fidelity measure. Nonmetric Multidimensional Scaling (NMDS) was used to explore the relationships between the distinguished groups. A total of five halophytic or subhalophytic grasslands, five halophytic thermophilous scrub communities, three hypersaline alluvial temporary flooded swards, and one riparian scrub community were distinguished in the study area, grouped in four orders. Four plant communities have been established as new associations: Knorringietum sibiricae, Puccinellietum pamiricae, Carici physodisZygophylletum gontscharovii and Zygophylletum ferganensis. The Taraxacion murgabici is described as new alliance of high-altitude halophytic vegetation in arid environments. The hypersaline alluvial temporary flooded swards were included in a new order – the Psylliostachyetalia spicato-leptostachyae. The main factors differentiating the species composition of the researched vegetation seem to be: the share and number of annual vs. perennial species, coverage of shrub layer, number and share of IranoTuranian plants, mean annual temperature, and altitudinal position. This is the first time we have initiated research on halophytic vegetation in Middle Asia. However, further geobotanical studies in this part of the world are needed, because the syntaxonomical position of some of the distinguished communities still remains vague.
Świerszcz, S., Nobis, M., Wróbel, A., Klichowska, E., Nowak, S. & Nowak, A. (2021): Halophytic vegetation and adjoining plant communities in Middle Asia (Pamir-Alai and western Tian Shan). – Tuexenia 41: 147–174.